What are the six steps involved in the sugar-coating process?

Sugar coating is when a layer of sugar or sucrose is applied over the core tablet, mainly to mask the taste. It’s the oldest technique used in pharmaceutical industries, and even though it’s a multistage and lengthy process, it’s been trusted for years. Depending on the formulation, the tablets can gain between 30-100% weight due to sugar coating. In fact, the history of coating materials for solid dosage forms dates back to Islamic literature, with Rhazes describing the coating of pills.
Principle of Sugar Coating
The principle of sugar coating is very simple which is as follows,
A solution of Sucrose or sugar is applied over rotating warm tablets and the solvent is evaporated by the application of Heat.
Role of Operator
Sugar coating is a detailed process that really hinges on the skills and experience of the person handling the operation. Unlike film coating, where an automatic system controls most of the parameters, sugar coating typically uses traditional methods where everything is done manually. The operator decides how much solution to apply with each coat, how fast the pan should move, how often to apply the coats, and the amount of heat needed. So, when it comes to conventional sugar-coating methods, having a skilled operator is absolutely crucial.
Although automation of sugar coating is also available in which sugar coating can be done in perforated pans using a solution delivery system in the form of nozzles there are the following drawbacks
- Choking of perforations
- Nonuniform delivery of solution due to high viscosity.
Because of the above drawbacks it is preferred to perform sugar coating in conventional coating pans.
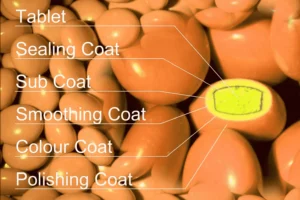
Steps of Sugar Coating
Sugar coating is not performed in a single step and the steps involved in the sugar coating process are as follows
- Sealing
- Sub-Coating
- Smoothing
- Colouring
- Polishing
- Printing
- Sealing
Sealing is also known as waterproofing, as the name indicates it is the stage that gives protection to the core tablet against water penetration.
Sealing or waterproofing is also used to give protection against moisture penetration.
In the Manual coating pan pouring method or pan ladling method there are chances of localized over-wetting due to the water present in the sucrose solution.
This over wetting of the tablet may result in softening of the tablet or may damage the tablet surface.
To prevent this damaging effect, a coat of sealing material in an organic solvent is applied.
On applying heat, the solvent evaporates leaving behind a layer of sealing material over the core tablet.
Seal coats in the automatic spraying process may be skipped by controlling the rate of application of the sub-coat.
So the application of seal coat is dependent on the formulation and equipment used.
The following are commonly used sealing materials
Shellac
Zein
HPC (Hydroxypropyl Cellulose)
CAP (Cellulose Acetate Phthalate)
Note:
When shellac is used as a sealing material it results in an increase in disintegration time on storage.
Zain is a protein obtained from corn and it does not affect disintegration time on storage.
Sub-Coating
Sub-coating is the first real step of sugar coating.
For sub-Coating less concentrated sucrose syrup is used.
This stage results in weight gain of the tablet and usually 50-100% gain in weight can be obtained.
This stage makes the edges of the tablet round.
Methods of Application
For the application of sub-Coat following two methods are used
Lamination Method
Suspension Method
Lamination Method
The lamination method may also be known as the dusting method because in this method powder materials like a mixture of powdered sugar and starch or talc and acacia are used for dusting.
A coat of binder solution is applied over hot tablets in a rotating pan.
Then dusting is done with powder materials and allowed to rotate in the pan to spread the powder uniformly.
After uniform distribution heat is applied to evaporate the water.
This process is repeated until the desired weight or thickness of the tablet is achieved.
Suspension Method
In the suspension method liquid sub-coating solution is used in the form of suspension.
The suspension may contain
- Gum solution
- Fillers like Calcium carbonate, talc,sucrose.
Fillers are added in a binder solution to form a suspension and then applied over the moving bed of the tablet.
Smoothing
The third step in sugar coating is smoothing.
Smoothing is also known as grossing or final rounding.
Tablets after the second stage of sub-coating are not smooth so to make tablets smooth the third stage or smoothing process is used.
Smoothing step is used to make the tablet surface smooth.
In smoothing, irregularity in tablet surfaces are filled to make it smooth.
For Smoothing concentrated sucrose solution is used.
Usually 70% sucrose syrup is used for this stage of smoothing.
In this stage a large volume of solution is not applied only 9 to 10 coats are enough to make the tablet surface smooth.
Coloring
In this stage a coat of specific color is applied over the tablets.
Color is applied by mixing it in a sucrose solution.
Color uniformity is one of the most important requirements of sugar coating.
So the color coat application should be done with great care.
🎓 Discover one of the best Quality assurance courses available — click below to explore the course that’s shaping future QA skills.

