
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 8, 2025
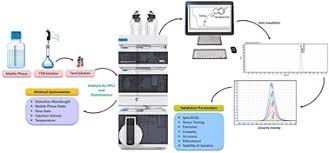
Why Analytical Method Validation is Required? Analytical Method Validation is essential to ensure that a test method is reliable, reproducible, and suitable for its intended purpose.It is required because: Regulatory Compliance Required by ICH Q2(R1), USFDA, EMA, and...
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 8, 2025
Steps for HPLC Method Development 1. Define the Purpose Identify the analyte(s) to be separated and quantified. Define method requirements (accuracy, precision, sensitivity, run time). 2. Gather Information Chemical structure, polarity, pKa, solubility of the analyte....
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 8, 2025
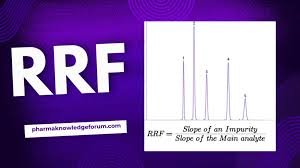
1. What is Relative Response Factor (RRF)? Definition: The Relative Response Factor is the ratio of the detector response of an analyte to that of a reference standard (usually the active ingredient or an internal standard), under identical chromatographic conditions....

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 8, 2025
Investigation of OOS Results in Analytical Testing 1. What is an OOS Result? An Out-of-Specification (OOS) result is any analytical test result that falls outside the established acceptance criteria/specifications outlined in an approved method, regulatory filing, or...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 8, 2025
Resolving API Impurity Issues in Drug Development 1. Understanding the Issue In drug development, impurities in the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) can arise from: Starting materials or intermediates (process-related impurities) By-products from synthesis steps...







