by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
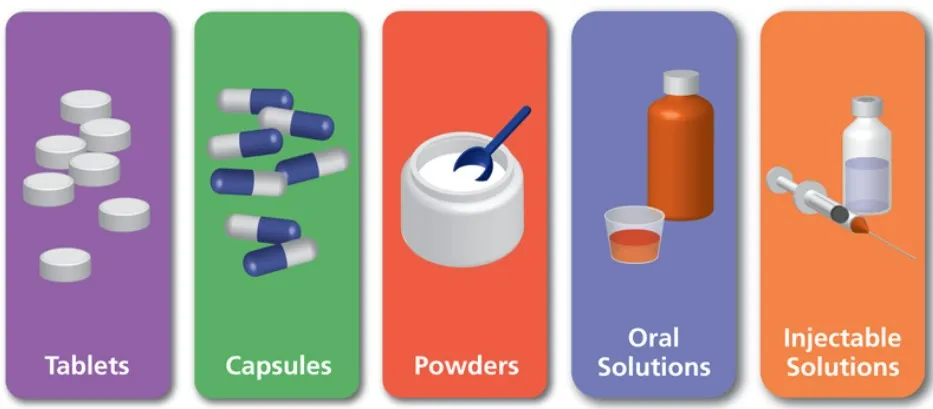
The Shape of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Definition:In pharmaceuticals, dosage form shape refers to the physical appearance and geometry of the medicine, which can influence patient compliance, swallowing ease, identification, and manufacturing efficiency. 1. Solid...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
Out of Specification (OOS) Investigation in Pharmaceuticals Definition OOS results are test results that fall outside the pre-established acceptance criteria defined in specifications, procedures, or regulatory filings.They can occur in raw materials, in-process...
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
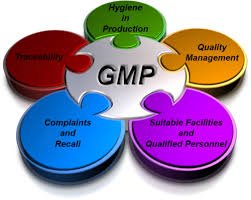
GMP Requirements in Pharmaceuticals Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is a regulatory framework ensuring that pharmaceutical products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards, minimizing risks to patients. 1. Quality Management System...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
Working Principle of a pH Meter Definition A pH meter is an analytical instrument used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration ([H⁺]) in a solution, expressing it as pH (potential of hydrogen). Principle A pH meter works on the electrochemical principle of measuring...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
Different Types of HPLC Detectors 1. UV/Vis Absorbance Detector Principle: Measures absorbance of analytes at a specific wavelength (Beer-Lambert Law). Types: Fixed Wavelength UV (e.g., 254 nm) Variable Wavelength UV Diode Array Detector (DAD/PDA) – allows spectral...







