
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 11, 2025
Calibration of Gas Chromatography (GC) 1. Introduction Gas Chromatography (GC) is used for separation, identification, and quantification of volatile and semi-volatile compounds. Calibration ensures that the GC system provides accurate, precise, and reproducible...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 11, 2025
HPLC Calibration Procedure 1. Introduction High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a critical analytical technique in pharmaceutical quality control. Regular calibration ensures accuracy, precision, and compliance with regulatory requirements like USP...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
Different Types of HPLC Detectors 1. UV/Vis Absorbance Detector Principle: Measures absorbance of analytes at a specific wavelength (Beer-Lambert Law). Types: Fixed Wavelength UV (e.g., 254 nm) Variable Wavelength UV Diode Array Detector (DAD/PDA) – allows spectral...
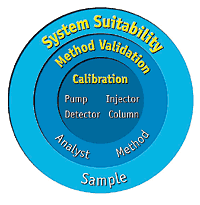
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 9, 2025
System Suitability in HPLC Analysis What is System Suitability? System Suitability Testing (SST) is a set of analytical checks performed before and during analysis to ensure that the HPLC system and method are capable of producing accurate, precise, and reproducible...







