
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Sep 6, 2025
1.0 Purpose To lay down the procedure for the safe, secure, and documented transfer of finished goods from the production/packing area to the bonded store room under controlled conditions to ensure compliance with regulatory and company requirements. 2.0 Scope This...
by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Sep 5, 2025
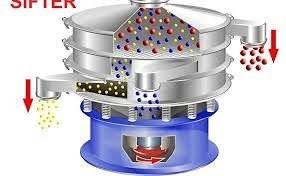
1.0 Purpose To define the procedure for operation, cleaning, and maintenance of the Vibro Sifter used in production to ensure efficient sieving of raw materials and granules as per cGMP requirements. 2.0 Scope This SOP applies to the Vibro Sifter installed in the...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 30, 2025
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Operation of Water Bath 1.0 Purpose To define the procedure for the correct operation of the water bath to ensure uniform and controlled heating of laboratory samples. 2.0 Scope This SOP applies to all Quality Control (QC),...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 27, 2025
Data Integrity in Microbial Analysis 1. Introduction In microbiology laboratories (especially in pharmaceutical QC/QA), data integrity ensures that all results of microbial testing are accurate, complete, consistent, and trustworthy throughout their lifecycle. Since...

by Dr. Yashashwini Reddy | Aug 18, 2025
Importance of Validation in Pharmaceuticals Validation in pharmaceuticals is a critical quality assurance tool that ensures products are consistently manufactured to meet predetermined specifications and regulatory requirements. Its importance can be summarized as...







