Fishbone Tool of Investigation in Pharmaceuticals
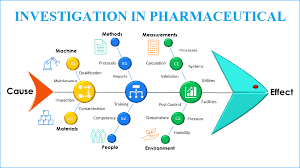
🐟 Fishbone Tool of Investigation in Pharmaceuticals
📌 What is It?
-
A cause-and-effect diagram shaped like a fish skeleton.
-
“Head” = problem statement (e.g., OOS result, contamination, deviation).
-
“Bones” = major categories of potential causes.
-
Helps investigation teams visualize, categorize, and analyze possible root causes systematically.
🧾 Common Categories in Pharmaceutical Investigations
Typically adapted into 6M model (can vary):
-
Man (Personnel)
-
Inadequate training or knowledge.
-
Human error (improper gowning, sampling mistakes).
-
Non-compliance with SOPs.
-
-
Machine (Equipment)
-
Equipment malfunction, improper calibration.
-
Poor preventive maintenance.
-
Design not suitable for cleaning.
-
-
Method (Procedures/SOPs)
-
Inadequate or unclear SOPs.
-
Not followed as written.
-
Lack of proper validation.
-
-
Material (Raw & Packaging)
-
Poor quality of raw materials or excipients.
-
Incorrect labeling or dispensing.
-
Supplier-related variability.
-
-
Measurement (Testing & Data Integrity)
-
Analytical method errors.
-
Incorrect instrument settings.
-
Data integrity lapses.
-
-
Mother Nature (Environment)
-
Environmental contamination (microbial, dust).
-
Temperature/humidity excursions.
-
Poor cleanroom classification or monitoring.
-
🔍 Steps in Using Fishbone for Investigation
-
Define the problem clearly (e.g., “High bioburden in water sample” or “Tablet hardness out of spec”).
-
Brainstorm possible causes under each category.
-
Populate the fishbone diagram with identified causes.
-
Analyze which causes are most likely using data, trend analysis, and evidence.
-
Identify the root cause(s) and link them to CAPA actions.
✅ Benefits in Pharma Investigations
-
Encourages team-based brainstorming.
-
Provides a structured and visual approach to RCA.
-
Ensures no potential cause is overlooked.
-
Strengthens compliance with FDA/ICH Q10 expectations for scientific investigation.
📌 Example Use Cases in Pharma
-
OOS result in HPLC assay.
-
Repeated microbial contamination in cleanroom.
-
Packaging mix-up investigation.
-
Equipment breakdowns affecting batch yield.
🎓 Discover one of the best Complete Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Course available —click below to explore the course that’s shaping future in QA Course skills.

