Deviation Control in Pharmaceuticals | Steps, Documentation, and GMP Compliance
Deviation Control in Pharmaceuticals
Definition:
A deviation is any departure from approved instructions, standard operating procedures (SOPs), specifications, or established Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements during manufacturing, testing, packaging, storage, or distribution of pharmaceutical products.
Deviations must be controlled to ensure that product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance are not compromised.
Types of Deviations
-
Planned Deviation
-
Authorized departure from an approved procedure or standard before execution.
-
Usually temporary and for a specific batch/period.
-
Example: Using an alternative raw material source in case of supply shortage.
-
-
Unplanned Deviation
-
Unexpected non-conformance occurring during operations.
-
Often discovered after occurrence.
-
Example: Temperature excursion during stability study.
-
Steps in Deviation Control Process
1. Detection & Reporting
-
Identify deviation during operations, audits, or testing.
-
Immediately inform the supervisor/QA.
-
Log the deviation in the Deviation Register or Quality Management System (QMS).
2. Initial Assessment
-
Determine:
-
Type (planned/unplanned)
-
Impact (minor, major, critical)
-
Potential risk to product quality, safety, or compliance.
-
-
Decide if production/testing should be stopped.
3. Documentation of Deviation
-
Record details in a Deviation Report:
-
Date/time of occurrence
-
Description of deviation
-
Batch/lot number (if applicable)
-
Equipment/materials involved
-
Personnel involved
-
Immediate action taken
-
4. Investigation
-
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) using tools like:
-
5 Whys
-
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
-
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
-
-
Involve cross-functional teams (Production, QC, QA, Engineering, etc.).
5. Impact Assessment
-
Evaluate effect on:
-
Product quality
-
Process validation status
-
Regulatory compliance
-
-
Assess batches affected and decide on disposition (release, reject, reprocess).
6. Corrective & Preventive Actions (CAPA)
-
Corrective Action: Fix the immediate problem.
-
Preventive Action: Modify process/SOP/training to prevent recurrence.
-
Implement changes after QA approval.
7. Review & Approval
-
QA reviews investigation, risk assessment, and CAPA.
-
Head of QA/Quality Unit authorizes closure of the deviation.
8. Closure
-
Update Deviation Log with closure date and summary of actions.
-
Archive records as per GMP retention policy.
Deviation Documentation Requirements (as per GMP)
-
Unique deviation number
-
Description of deviation
-
Date/time, location, and personnel
-
Batch/lot number (if applicable)
-
Immediate corrective action taken
-
Root cause and investigation details
-
Risk/impact assessment
-
CAPA details
-
QA review and approval
-
Signatures and dates
GMP Compliance Points
-
All deviations must be reported immediately—no undocumented fixes.
-
Deviation procedure must be approved in SOP form and followed consistently.
-
Classification of deviations (minor/major/critical) should be defined.
-
QA must be involved in investigation and closure.
-
Documentation should be accurate, contemporaneous, legible, original, attributable (ALCOA principles of data integrity).
-
Trends of deviations must be periodically reviewed for continuous improvement.
-
Regulatory bodies (US FDA, EMA, WHO) expect deviation control to be robust, traceable, and risk-based.
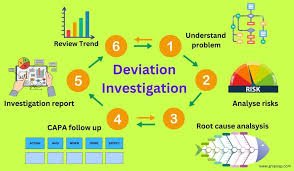
✅ Example of Deviation Flow (Simplified):
Detection → Reporting → QA Notification → Investigation & RCA → Impact Assessment → CAPA → QA Review → Closure → Trending & Continuous Improvement.
🎓 Discover one of the best Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance course available —
click below to explore the course that’s shaping future Quality Assurance skills.
https://trcjw.on-app.in/app/oc/306166/trcjw

