Allergen Control Plan for Pharmaceuticals
🧾 Allergen Control Plan for Pharmaceuticals
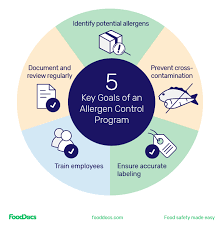
1. Risk Assessment
-
Identify allergenic excipients (e.g., lactose, soy lecithin, egg-derived albumin, peanut oil, gluten, gelatin).
-
Assess risk of cross-contamination during manufacturing, packaging, storage, and cleaning.
-
Evaluate suppliers for allergen management in raw materials.
2. Raw Material & Supplier Control
-
Maintain an allergen inventory with details of all incoming materials.
-
Require allergen declarations and certificates from suppliers.
-
Segregate allergen-containing materials in dedicated storage areas with clear labeling.
3. Facility & Equipment Design
-
Where possible, use dedicated equipment and manufacturing areas for allergen-containing products.
-
Apply physical segregation (barriers, color-coded equipment, separate gowning).
-
Maintain proper HVAC systems to prevent airborne cross-contamination.
4. Cleaning & Sanitation Controls
-
Establish validated cleaning procedures to remove allergenic residues.
-
Perform swab testing and analytical verification (e.g., ELISA-based allergen detection).
-
Define “cleaning verification vs cleaning validation” requirements specific to allergens.
5. Production & Handling Practices
-
Schedule allergen-containing product manufacturing at the end of production cycles where feasible.
-
Implement strict line clearance procedures before and after allergen handling.
-
Control waste handling and prevent re-entry of contaminated materials.
6. Personnel Practices
-
Train employees on allergen awareness, handling, and prevention of cross-contact.
-
Use dedicated gowns, gloves, and tools when working with allergenic materials.
-
Ensure proper hygiene and gowning procedures before moving between production areas.
7. Labeling & Documentation
-
Clearly label allergen-containing materials and products at every stage.
-
Ensure patient information leaflets and packaging mention allergenic excipients as per regulatory requirements (e.g., lactose intolerance, peanut oil warnings).
-
Maintain traceability records for allergen management.
8. Deviation, CAPA & Monitoring
-
Investigate any allergen cross-contamination incident as a critical deviation.
-
Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) with root cause analysis.
-
Periodically audit allergen control practices and update risk assessments.
9. Regulatory Compliance
-
Align with ICH Q9 (Quality Risk Management), EU EMA excipient guidelines, US FDA labeling requirements, and WHO GMP expectations.
-
Ensure compliance with local pharmacopeia labeling requirements for allergens.
📌 Key Benefits of an Allergen Control Plan
-
Prevents patient safety risks (hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis).
-
Reduces risk of regulatory non-compliance and recalls.
-
Supports data integrity and transparency in product labeling.
-
Enhances patient trust and product quality.
🎓 Discover one of the best Complete Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Course available —click below to explore the course that’s shaping future in QA Course skills.

