What is Pitot Tube | Insertion flow Meter; Principle, Construction, and Working
📌 Pitot Tube | Insertion Flow Meter
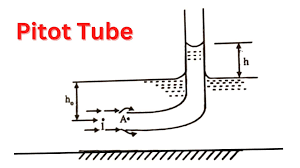
A Pitot tube (also called an Insertion Flow Meter) is a simple, low-cost device used to measure the fluid velocity in pipelines, ducts, or open channels. It works on the principle of differential pressure measurement between stagnation and static pressure points.
🔬 Principle of Pitot Tube
-
Based on Bernoulli’s principle:
-
When fluid strikes the open end of the tube (stagnation point), it comes to rest, and pressure increases (stagnation pressure).
-
At the side openings, fluid continues to flow, showing only static pressure.
-
The difference between stagnation and static pressure = dynamic pressure, which is directly related to fluid velocity.
-
V=2ΔPρV = \sqrt{\frac{2 \Delta P}{\rho}}
Where:
-
VV = Fluid velocity
-
ΔP\Delta P = Pressure difference (stagnation – static)
-
ρ\rho = Fluid density
⚙️ Construction of Pitot Tube
-
Tube: A slender tube with two openings:
-
Front opening → measures stagnation pressure.
-
Side openings → measure static pressure.
-
-
Insertion Mechanism: Tube inserted directly into the pipeline or duct.
-
Manometer/Transmitter: Connected to measure the pressure difference.
-
Support Structure: Mounting arrangements for ducts/pipes.
🔄 Working of Pitot Tube
-
Inserted into the pipeline with its front opening facing the fluid flow.
-
The stagnation pressure is sensed at the front opening.
-
The static pressure is sensed from side holes.
-
The pressure difference is measured using a differential manometer or transmitter.
-
Using Bernoulli’s equation, the fluid velocity is calculated.
-
Multiplying velocity by the cross-sectional area of the pipe gives the volumetric flow rate.
🏭 Applications in Pharmaceuticals & Industry
-
Measuring air velocity in HVAC ducts.
-
Flow measurement in compressed air, steam, and gas lines.
-
Monitoring exhaust air in cleanrooms.
-
Measuring velocity in large pipelines where installing a full-bore flowmeter is not economical.

