Use of lon Exchange Resins in Water Purification Systems
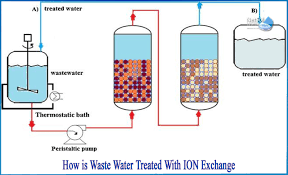
Use of Ion Exchange Resins in Water Purification Systems
Ion exchange resins are insoluble, cross-linked polymer beads with functional groups that can exchange specific ions from water, effectively removing unwanted dissolved salts, minerals, or contaminants. They are widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and laboratory water systems to achieve the required water purity.
Types of Ion Exchange Resins
-
Cation Exchange Resins
-
Contain acidic functional groups (e.g., sulfonic acid groups).
-
Exchange positive ions (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Na⁺) with H⁺ ions.
-
-
Anion Exchange Resins
-
Contain basic functional groups (e.g., quaternary ammonium groups).
-
Exchange negative ions (Cl⁻, SO₄²⁻, NO₃⁻) with OH⁻ ions.
-
Working Principle
-
Cation exchange replaces positively charged ions in water with hydrogen ions.
-
Anion exchange replaces negatively charged ions with hydroxyl ions.
-
H⁺ and OH⁻ combine to form pure water (H₂O).
-
Often arranged in mixed-bed resins for high-purity water.
Applications in Water Purification
-
Pharmaceutical industry – Purified water (PW) and Water for Injection (WFI) preparation.
-
Boiler feed water – Prevents scaling and corrosion.
-
Food and beverage – Softening and demineralizing water.
-
Laboratories – Ultra-pure water for analytical techniques (HPLC, GC, spectroscopy).
Advantages
-
Produces high-purity water.
-
Regenerable and reusable.
-
Compact and efficient design.
Limitations
-
Limited capacity before regeneration is required.
-
Sensitive to fouling from organics, particulates, or bacteria.
-
Requires periodic regeneration with acid/alkali.

