“Comprehensive Guide to Sampling and Testing in Exhibit and Process Validation Batches”

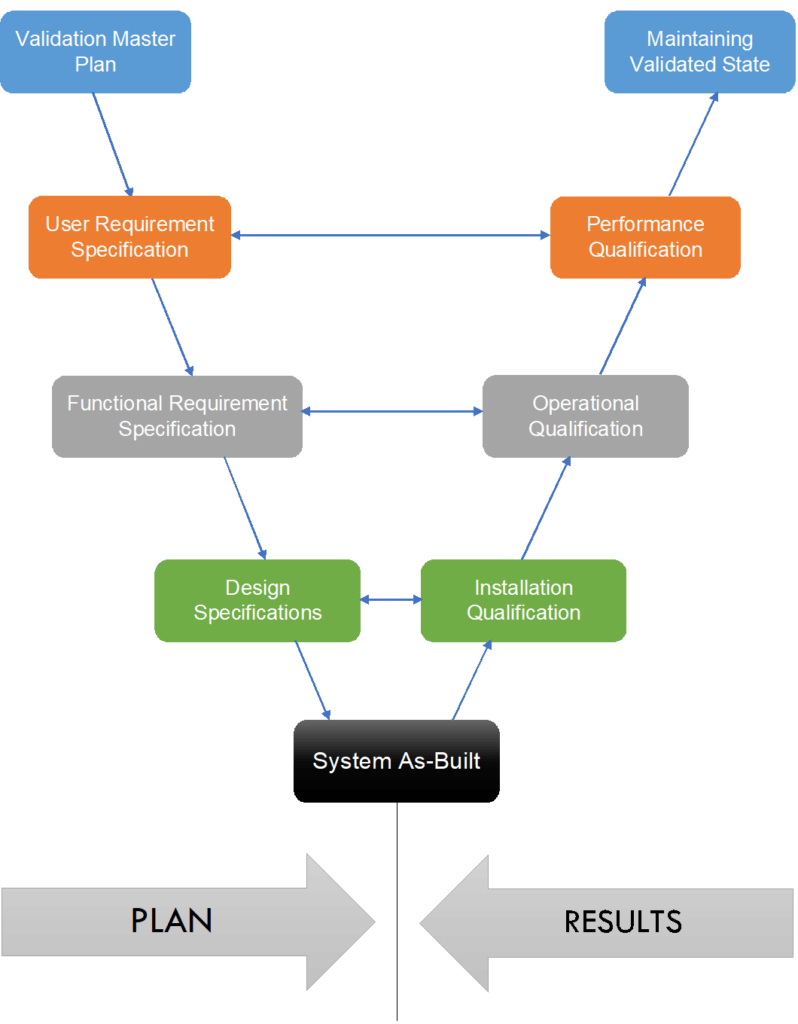
Sampling and Testing in Exhibit and Process Validation Batches
Sampling and testing are pivotal components in the pharmaceutical industry’s process validation framework. They ensure that manufacturing processes consistently yield products meeting predefined quality standards. This practice is integral to demonstrating that a process is capable of producing a product of desired quality and consistency.
1. Purpose of Sampling and Testing
-
Demonstrate Process Consistency: Sampling and testing provide evidence that the manufacturing process consistently produces products that meet predetermined specifications.
-
Identify Variability: They help in detecting variations within and between batches, ensuring that any deviations from quality standards are identified and addressed promptly.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to established sampling and testing protocols is essential for meeting regulatory requirements set by authorities such as the FDA and EMA.
2. Types of Validation Batches
-
Exhibit Batches: These are produced to support regulatory submissions and demonstrate the manufacturing process’s capability to produce a product meeting quality standards.
-
Process Validation Batches: Conducted to confirm that the manufacturing process can consistently produce a product meeting its specifications.
3. Sampling Strategies
-
Blend Sampling: Involves taking samples from various locations within the blend to ensure uniformity. For instance, in tumbling blenders, samples should be taken from different depths along the blender’s axis.
-
Dosage Unit Sampling: Samples are taken from the final dosage form to assess uniformity and content uniformity. This includes sampling at different stages of the process, such as hopper changeovers and machine shutdowns.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Sampling of the manufacturing environment to detect any potential contaminants that could affect product quality.
4. Testing Protocols
-
Analytical Testing: Includes tests for identity, potency, purity, and other critical quality attributes (CQAs) to ensure the product meets its specifications.
-
Microbiological Testing: For products where microbial contamination is a concern, microbiological testing is conducted to ensure the product is free from harmful microorganisms.
-
Stability Testing: Samples from validation batches are subjected to stability studies to assess the product’s shelf life and storage conditions.
5. Acceptance Criteria
-
Statistical Justification: Sampling plans and acceptance criteria should be statistically based, ensuring that the sample size and sampling locations are adequate to detect variability.
-
Homogeneity Assessment: Tests should demonstrate that the product is homogeneous throughout the batch, ensuring consistent quality in every unit.
-
Compliance with Specifications: All test results should comply with the predefined specifications to confirm the process’s capability.
6. Documentation and Reporting
-
Sampling Records: Detailed records of sampling locations, times, and personnel involved are essential for traceability and accountability.
-
Test Reports: Comprehensive reports documenting the testing procedures, results, and any deviations observed during the validation process.
-
Deviation Management: Any deviations from the established protocols should be documented, investigated, and addressed through corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
7. Regulatory Considerations
-
Compliance with Guidelines: Ensure adherence to regulatory guidelines such as ICH Q7, FDA 21 CFR Part 211, and EMA guidelines for process validation.
-
Justification of Sampling Plans: Provide scientific justification for the number of batches, sampling locations, and testing methods used during validation.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Implement a system for ongoing monitoring and revalidation to ensure the process remains in a state of control throughout its lifecycle
In summary, effective sampling and testing in exhibit and process validation batches are crucial for ensuring that pharmaceutical products are consistently of high quality. By adhering to scientifically justified protocols and maintaining rigorous documentation, manufacturers can demonstrate the reliability and consistency of their manufacturing processes, thereby ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
🎓 Discover one of the best Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance course available — click below to explore the course that’s shaping future Quality Assurance skills.

